HTAP Databases notes
Preliminary
Gartner’s definition in 2014: utilizes in-memory computing technologies to enable concurrent analytical and transaction processing on the same in-memory data store
Gartner’s new definition in 2018: supports weaving analytical and transaction processing techniques together as needed to accomplish the business task.
可以看到不再局限于in-memory
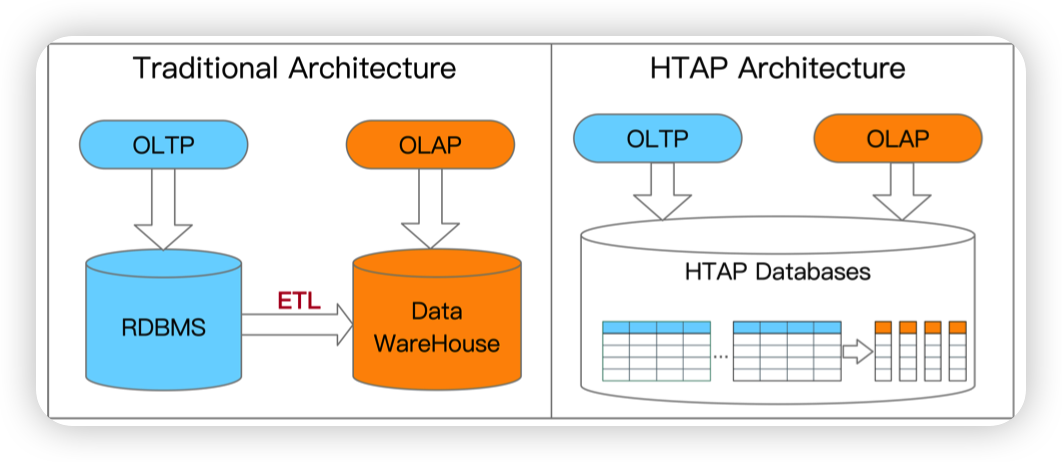
传统架构是从数据库中通过ETL导入到数据仓库中,然后做AP
HTAP数据库避免了ETL的流程,并且可以支持实时的数据分析,提高了数据的新鲜度
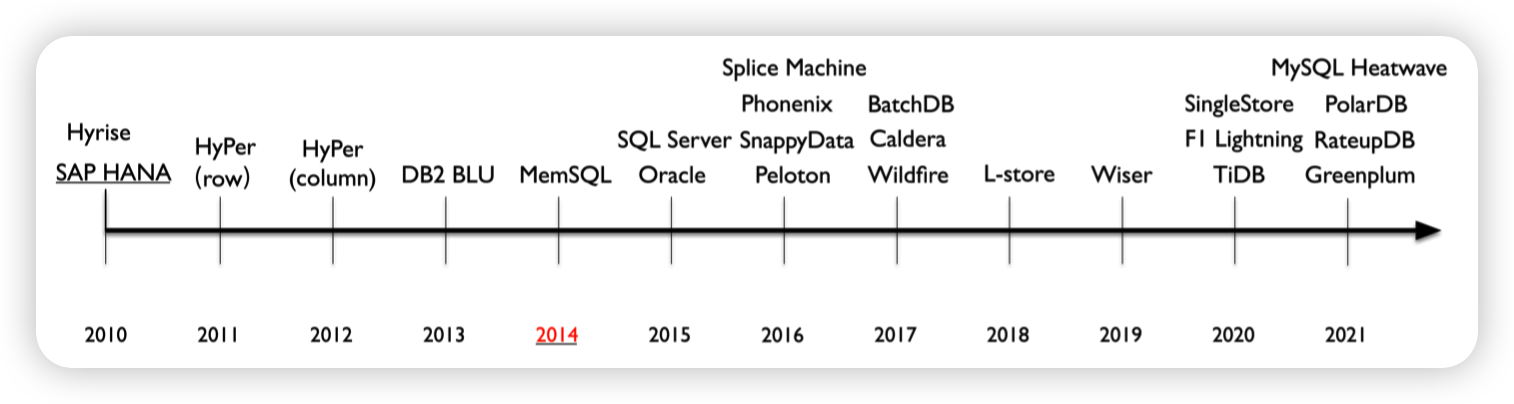
过去的十年中,HTAP数据库分为3个阶段:
- Phase 1 (2010-2014): HTAP databases mainly adopt primary column store
- Phase 2 (2014-2020): HTAP databases mainly extend the primary row store
- Phase 3 (2020-present): HTAP databases utilize a distributed architecture
Trade-Off
- Workload isolation: the isolation level of handling the mixed workloads
- Data freshness: the portion of latest transaction data that is read by OLAP
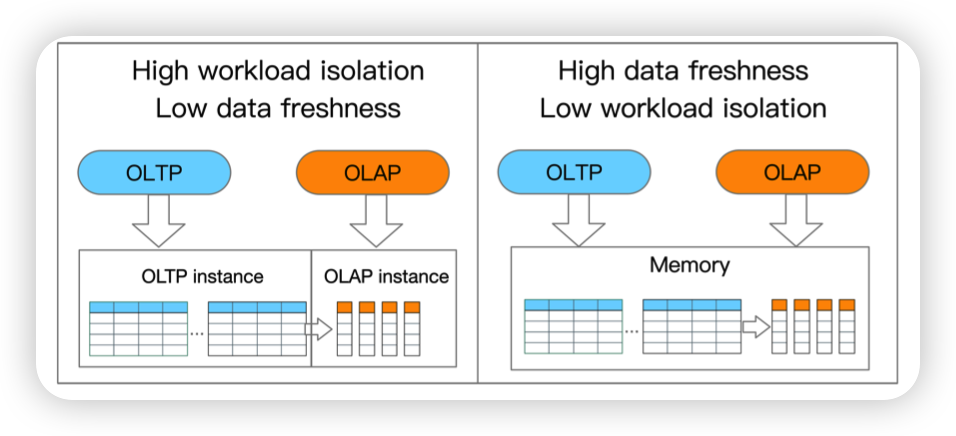
这里的意思是把AP和TP任务放到同一个机器上,数据的新鲜度肯定比较高,但是缺点就是可能导致资源的争抢。
或者是将不同类型的任务放到不同的实例上,资源就可以隔离开,这样数据的转换传输就需要一定的时间,降低了数据的新鲜度。
Challenge
- Challenge 1 (Data Organization): how to organize the data adaptively for HTAP workloads with high performance and low storage cost.
- Challenge 2 (Data Synchronization): how to synchronize the data from the row store to the column store for high throughput and data freshness
- Challenge 3 (Query Optimization): how to optimize the query with both row store and column store by exploring the huge plan space.
- Challenge 4 (Resource Scheduling): how to schedule the resources for OLTP and OLTP instances effectively for high throughput and data freshness.
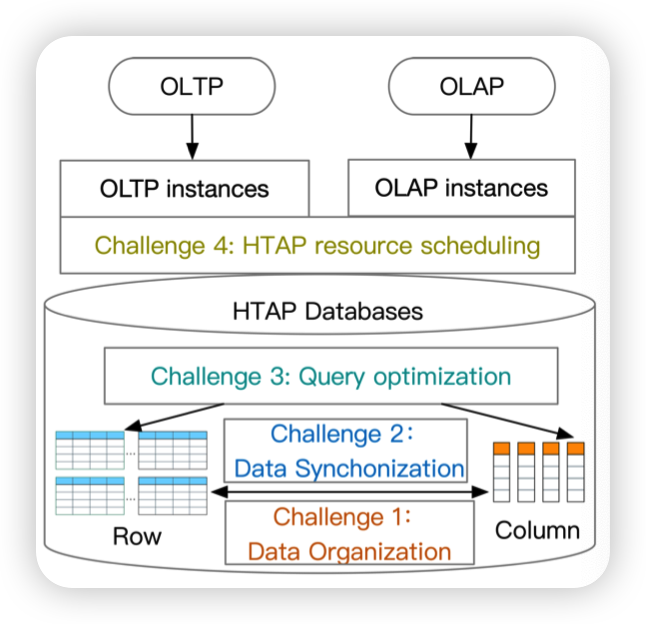
上面四点challenge,对应到图上就比较清楚。如何组织数据,不同数据格式之间的转换,优化器可能需要从row store以及column store中结合起来查数据,就需要有更好的策略做查询优化,以及资源的调度,合理利用CPU以及存储资源
HTAP Databases
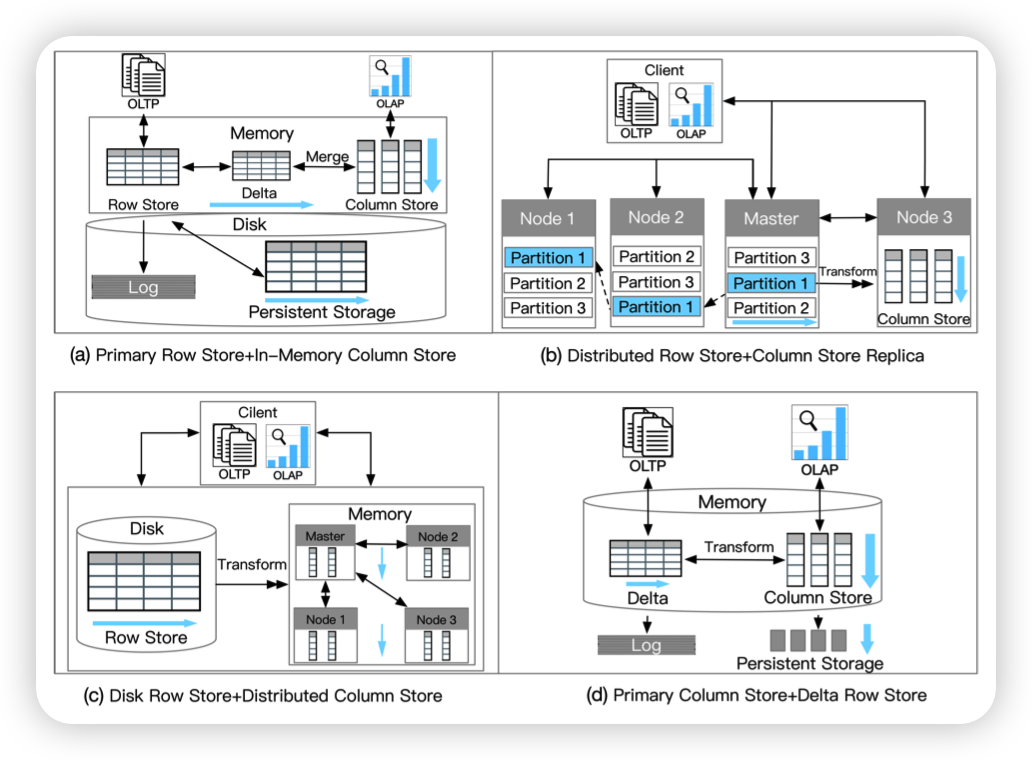
四种架构:
- Primary Row Store + InMemory Column Store
- Distributed Row Store + Column Store Replica
- Disk Row Store + Distributed Column Store
- Primary Column Store + Delta Row Store
一个一个看一下
Primary Row Store + In Memory Column Store
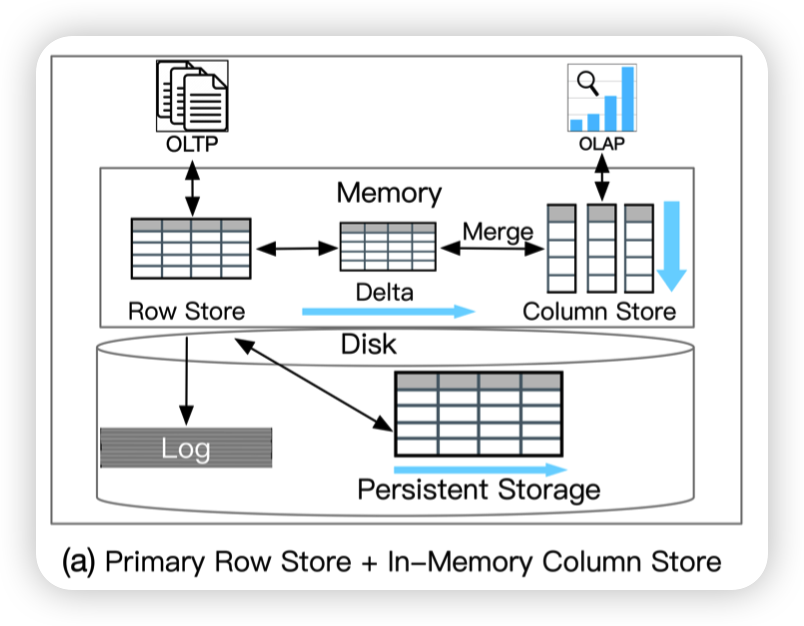
是单机引擎。在内存中拓展了原本的RowStore。在更新RowStore的时候,生成一个Delta出来,然后Merge到ColumnStore中。
当然肯定要有一定的聚合,否则ColumnStore也跟不上RowStore的更新速度...
好处就是不会影响到TP的吞吐,同时ColumnStore也在内存中,所以AP的吞吐也会比较高。并且由于是在同个机器中,随着Delta Merge的频率的改变可以达到比较高的数据新鲜度。
缺点就是ColumnStore都在内存中,所以受限于机器资源,无法scale out。并且负载隔离做的也不好。AP和TP之间会相互影响,导致资源的争夺。
特点就是High throughput, low scalability,他这里给了个应用banking with real-time data analytics
Oracle Dual-Format
| Oracle database in-memory: A dual format in-memory database

SQL Server
Real-time analytical processing with SQL server
Trekking through Siberia: Managing cold data in a memory-optimized database
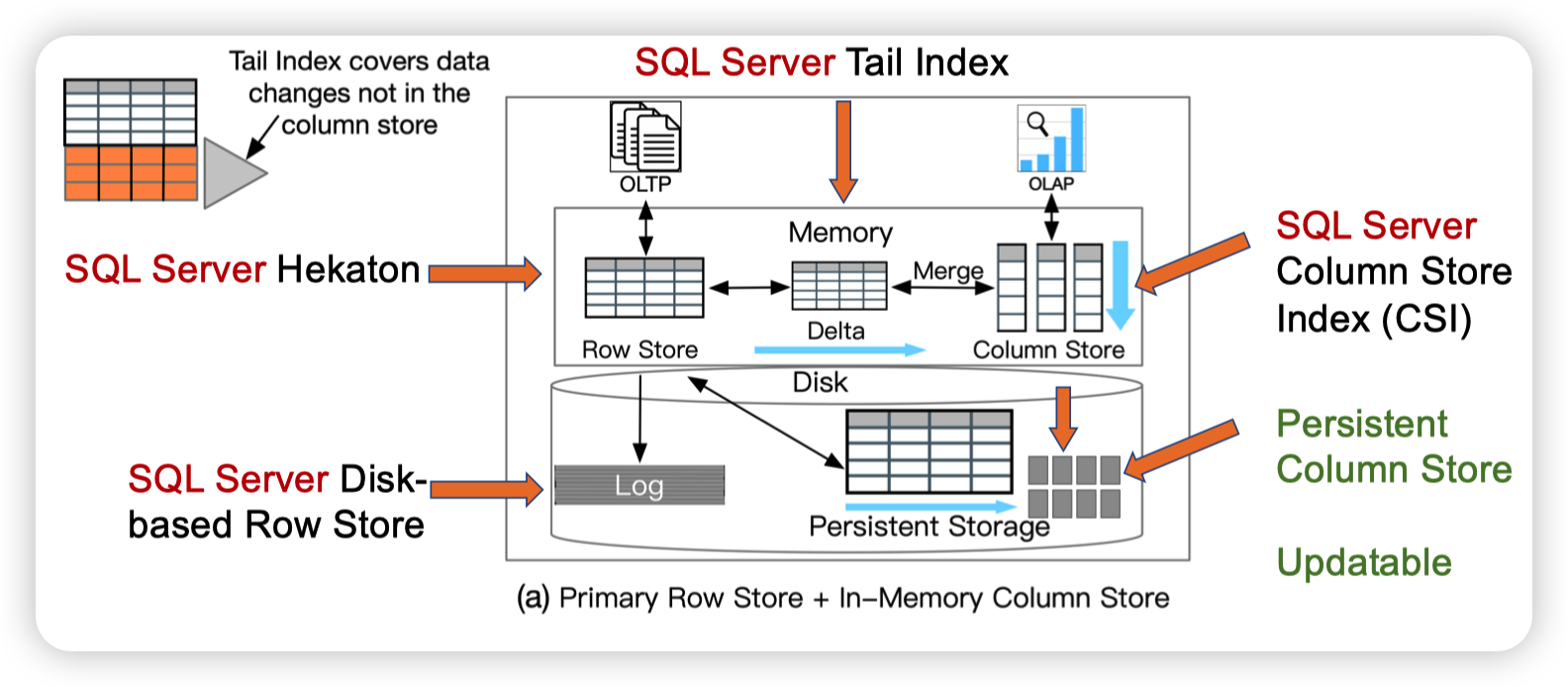
SQL Server通过tail index来记录那些没有被merge到列存的数据。这样AP就可以通过tail index找到最新的数据。
Transaction Processing On Modern Hardware上也提到过他们基于Hekaton做了一些冷热数据划分的功能。应该和这个Persistent Column Store有一定的关系。
Distributed Row Store + Column Store Replica

Shared Nothing架构。每个节点负责若干个Partition。让某一个副本转换成列存,提供AP服务。上层的AP查询可以通过结合列存副本加上主副本的数据得到最新的数据。
个人感觉就是一些特殊的节点读区快照转化成列存的形式。不太清楚是加入到了raft group中作为特殊的节点提供服务还是与共识协议隔离开。
好处就是可以scale out,并且可以隔离资源。这样有的节点负责作为Leader写入,有的节点负责作为列存提供AP服务。
缺点就是数据同步开销会比单机的大一些,数据新鲜度没那么高。
特点就是High TP & AP scalability, tolerable data freshness,这里的例子是E-commerce with real-time data analytics
F1 Lightning
F1 Lightning: HTAP as a Service
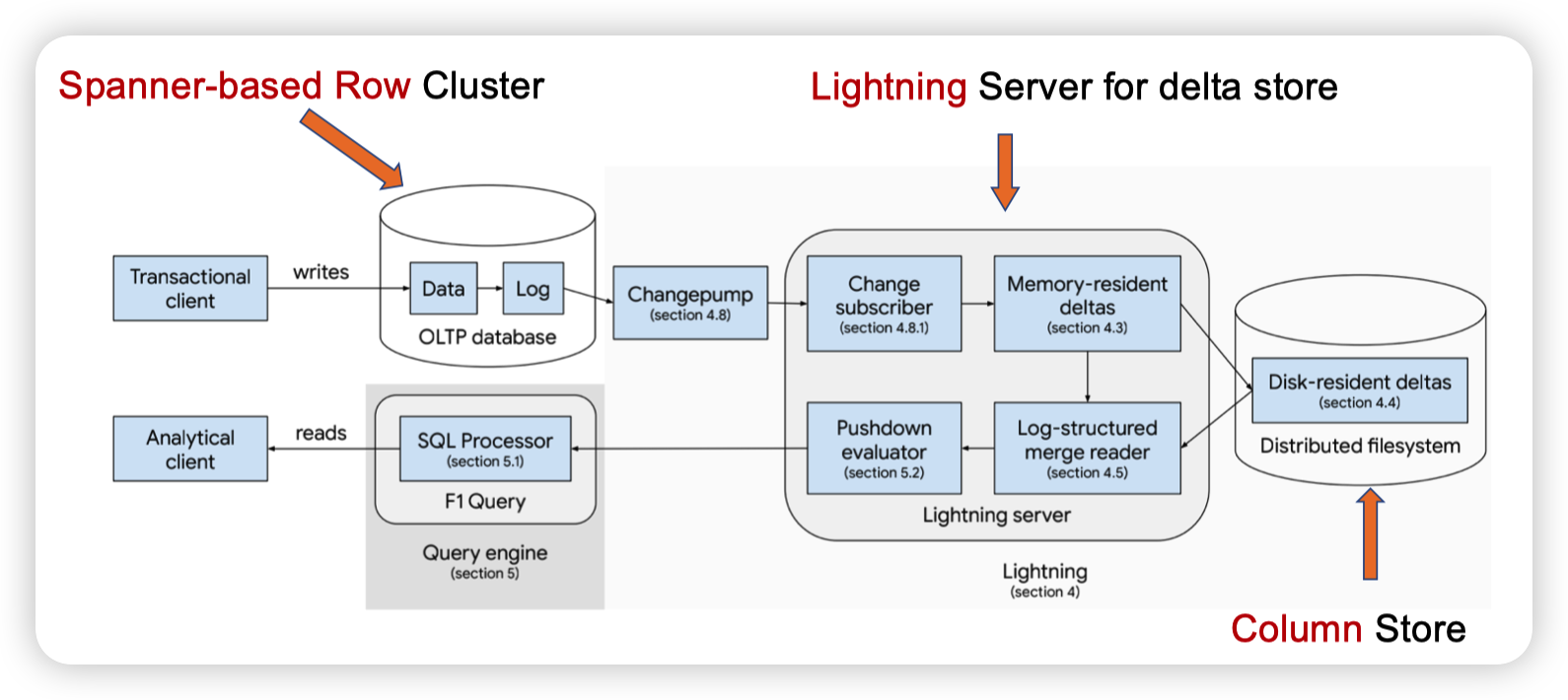
看起来订阅Spanner的log,然后转化成Delta。并且和底层的ColumnStore中的数据合并起来做计算,从而提供AP的服务。
TiDB
TiDB: a Raft-based HTAP database
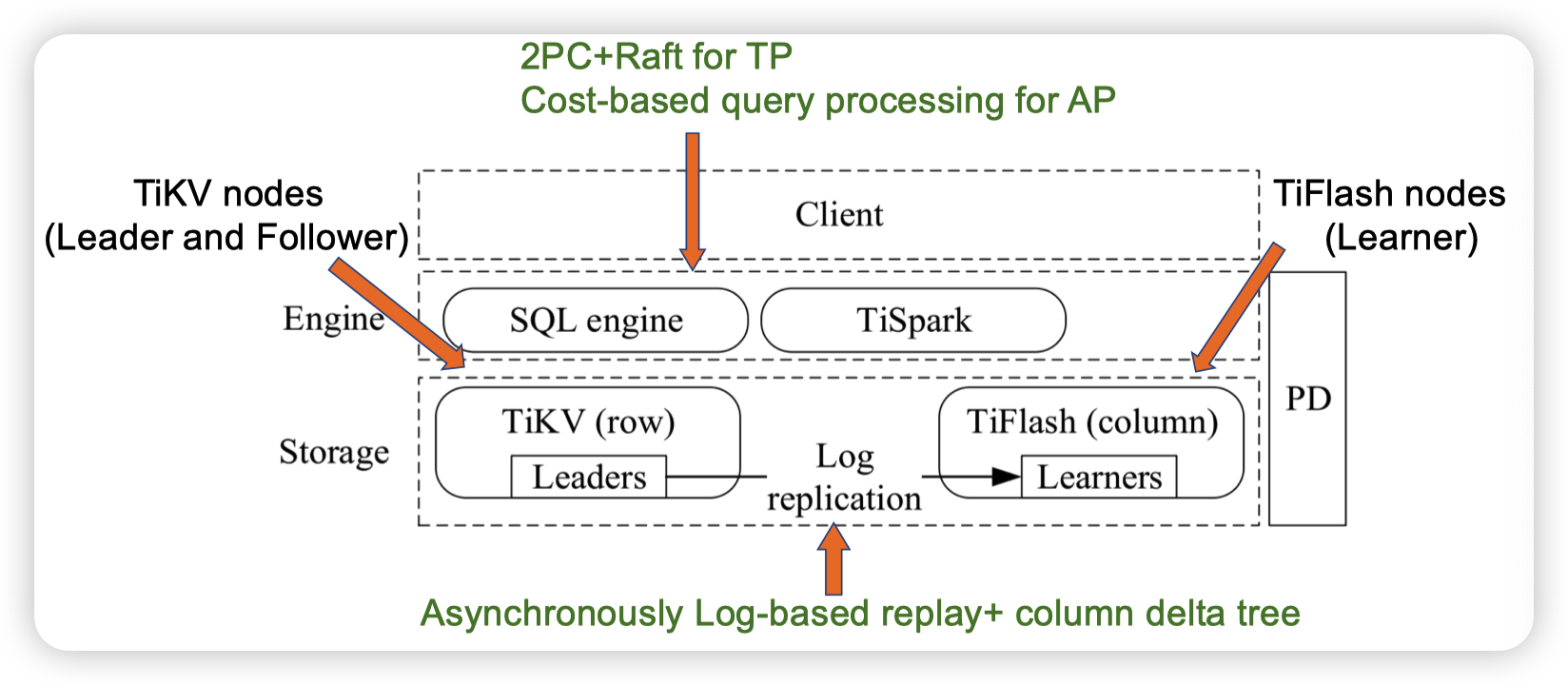
TiFlush通过重放TiKV的log来构建ColumnStore。TiFlash我猜应该是作为只读的learner订阅raft log,应该不作为raft group的member,因为他不可能成为主节点。
Disk Row Store + Distributed Column Store
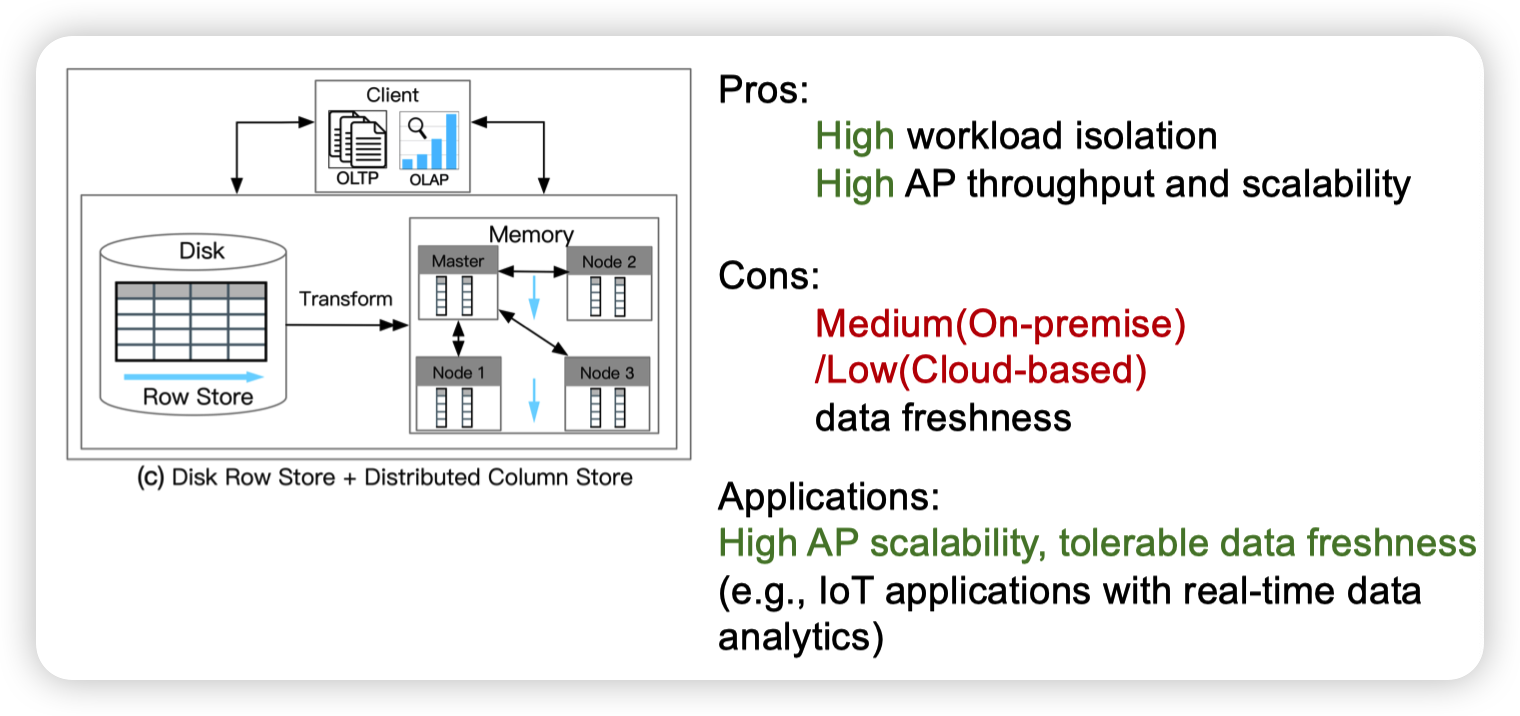
这个感觉就是刚才第一种方式的一个优化版了,为了解决AP不能scale out的问题。
当然分布式会引入一定的同步开销,导致数据新鲜度会差一些。
对于原本的行存数据库没什么影响,思路大概是拓展现有成熟的数据库MySQL,PG什么的。
特点就是High Ap scalability, tolerable data freshness,例子则是IoT applications with real-time data analytics
MySQL Heatwave
MySQL Heatwave. Real-time Analytics for MySQL Database Service

200ms或者delta达到64mb的时候,将delta同步给Heatwave集群。他们负责merge delta,并提供AP服务。
Oracle RAC
Oracle database in-memory: A dual format in-memory database
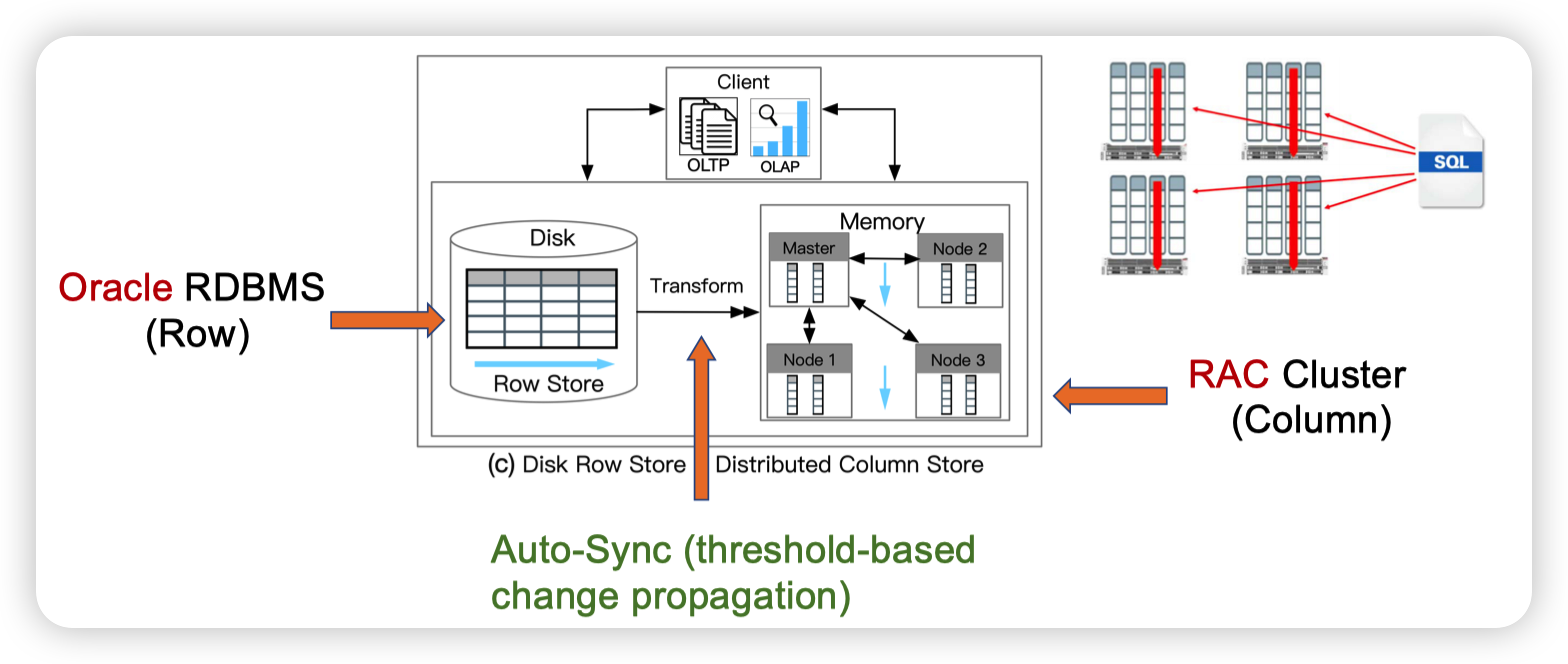
这里可能就是Oracle为了解决AP不能scale out的一个方法。就是把内存中的column store做分片,给到不同的机器上。
不太清楚他们部署的情况,如果是一个机器做TP,其他的机器做AP感觉有点奇怪。但是如果是多个机器混合TP和AP就有点shared nothing那种感觉了。
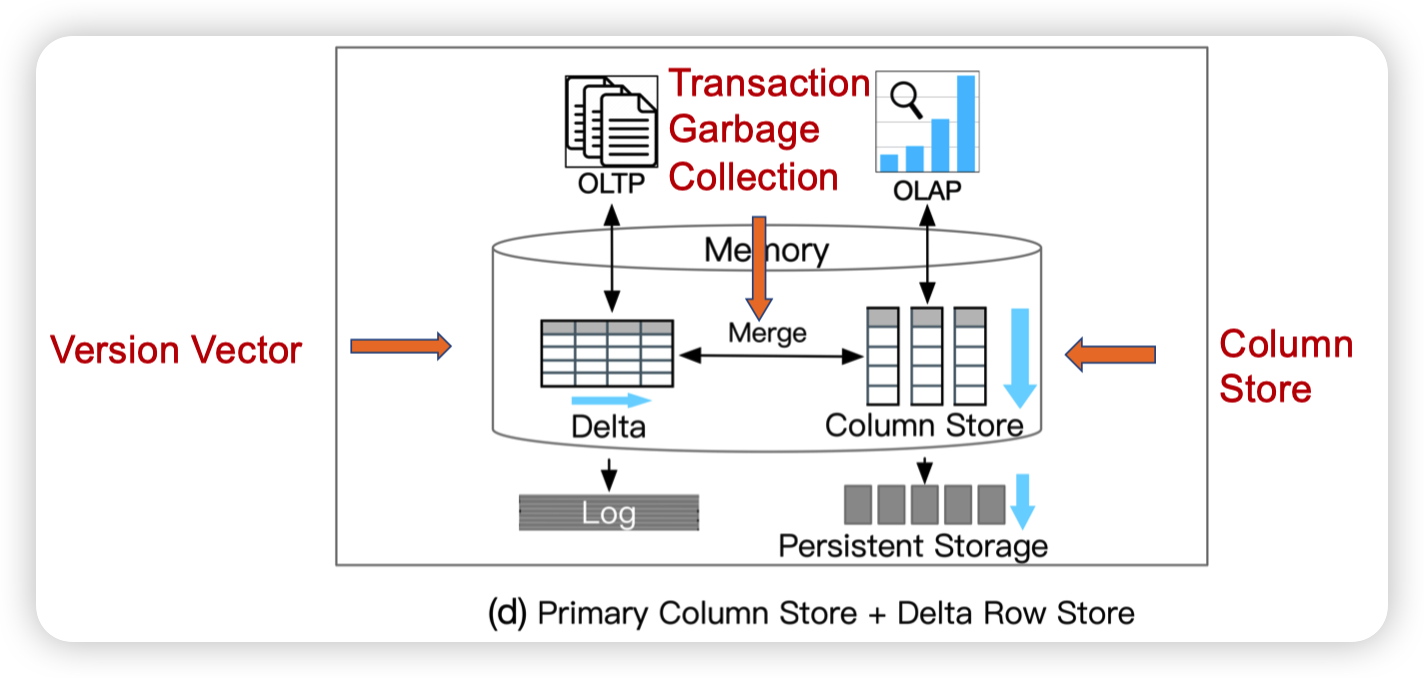
Primary Column Store + Delta Row Store

主列存,Delta做行存。偏向AP。
好处就是AP的性能和新鲜度都可以很高。
缺点就是TP的拓展性比较差,Delta不能支持很高的TP吞吐。并且也有单机引擎的限制就是资源的隔离。
特点就是High AP throughput, High data freshness,例子则是Real-time Fraud Detection
SAP HANA
Efficient transaction processing in SAP HANA database: the end of a column store myth
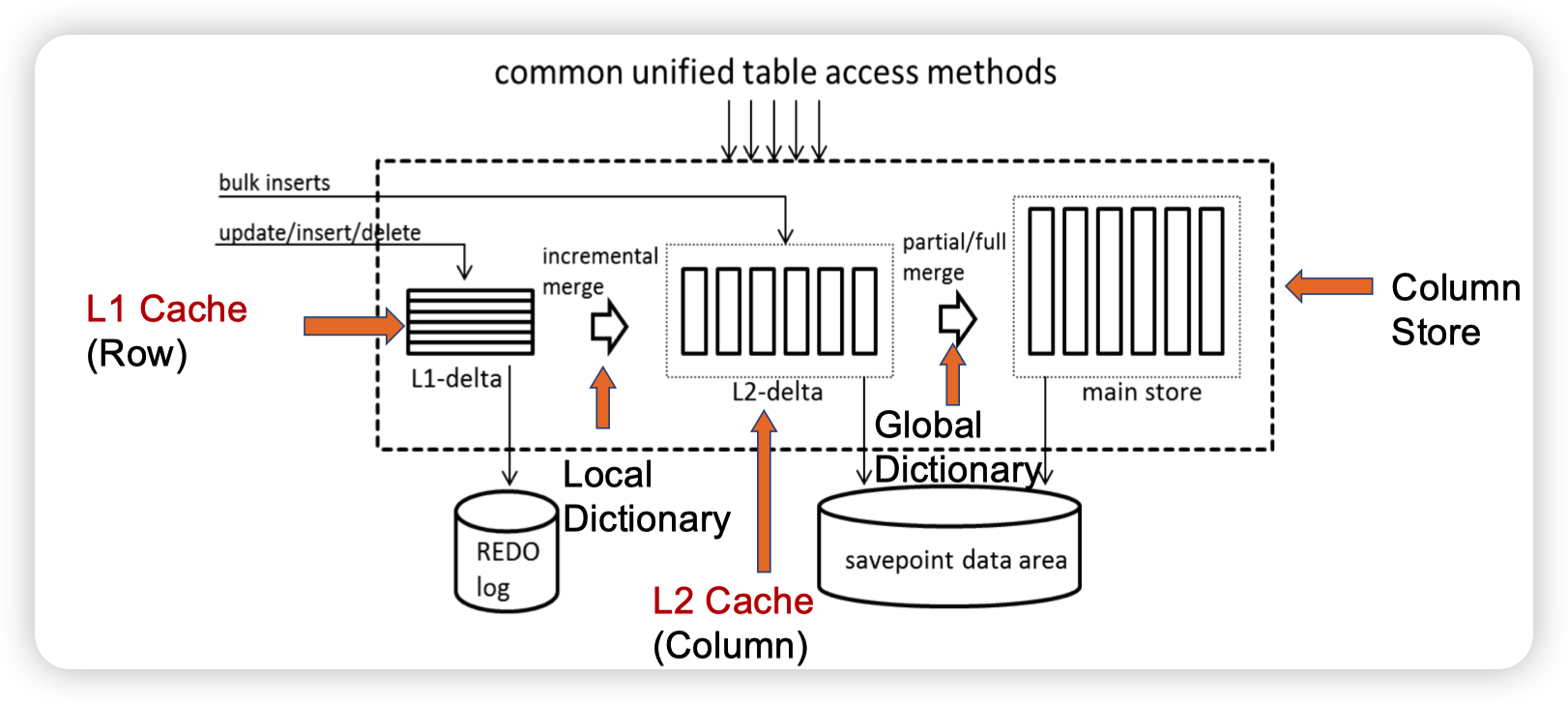
思路就是正常的更新会放到L1-delta中,写入redo log。然后和bulk insert(聚合更新)来做merge,得到一个更大规模的delta,这里就会变成列存的形式。然后再根据全局的索引来和整个的ColumnStore做merge。
Hyper
Fast serializable multi-version concurrency control for main-memory database systems
这个引用应该还有一些别的。2015年这篇比较偏向MVCC,而非AP。并且这篇论文里他们也没有用Delta做merge。而是直接存多版本的数据。
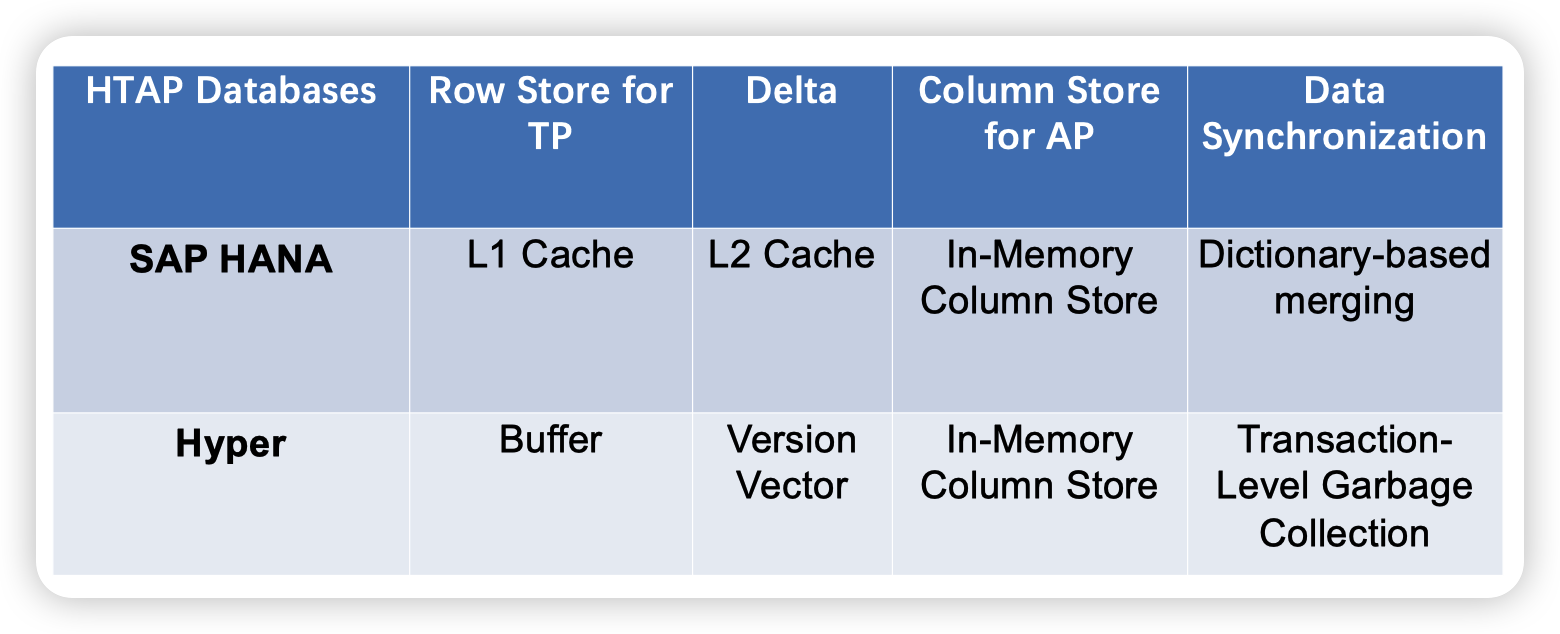
slides里说hyper的同步方式是通过GC。感觉有点不太对劲,hyper应该是直接写到列存中。
Other HTAP Systems
Row-based HTAP systems
- Hyper: support HTAP with copy-on-write mechanism
HyPer: A hybrid OLTP&OLAP main memory database system based on virtual memory snapshots
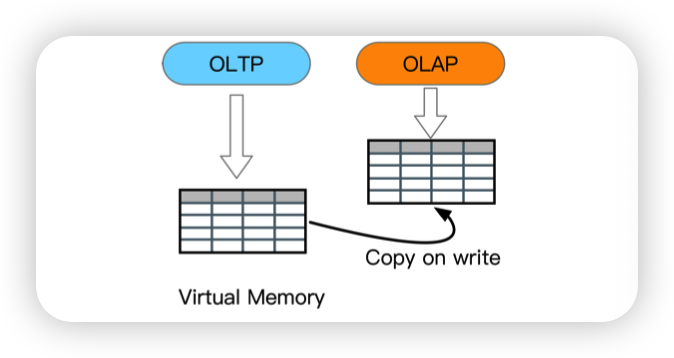
这个说的是AP的时候fork一个进程出来。相当于是获取了一个全局快照。
感觉没啥用...
- BatchDB: row-based dual-store with batched workload scheduling
BatchDB: Efficient isolated execution of hybrid OLTP+ OLAP workloads for interactive applications
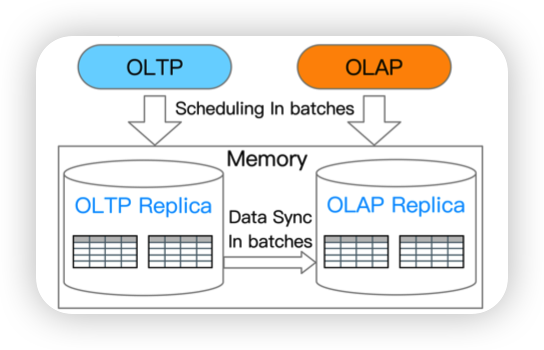
TP的时候攒一批数据在AP的实例上重放。有点诡异的是既然都重放了,为什么不重构出列存呢
Column-based HTAP systems
- Caldera: copy-on-write column store with CPU/GPU architecture
The case for heterogeneous HTAP
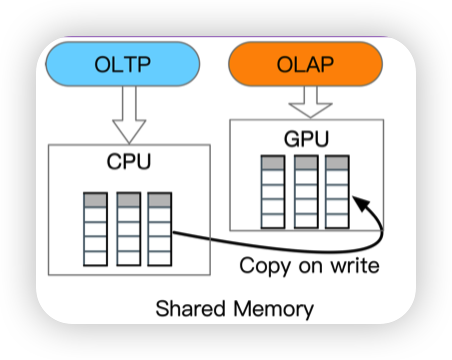
和Hyper不同的是,COW的时候的新的进程会让GPU来处理
- RateupDB: column-based dual-store with CPU/GPU architecture
The art of balance: a RateupDB™ experience of building a CPU/GPU hybrid database product

也是异构的,TP的数据同步到AP的副本上。然后让GPU来处理。
感觉这种格式相同不同副本主要的目的是为了提供一个一致性的快照,否则的话AP的代码里就要处理很多事务相关的逻辑
Spark-based HTAP systems
- Splice Machine: loosely couple HBase with Spark
https://splicemachine.com/blog/defining-htap/
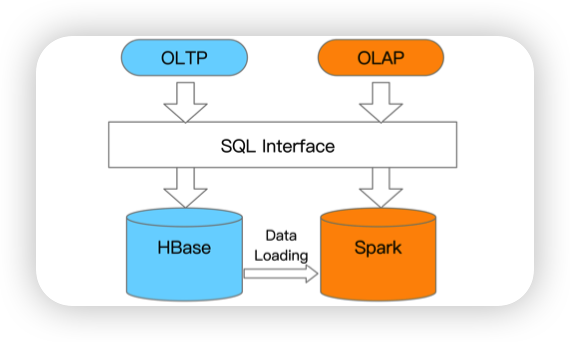
通过HBase做TP,然后把数据导入到Spark里,然后做AP。上面提供一个统一的接口。
感觉和走ETL的传统流程没什么区别..
- Wildfire: tigetly couple OLTP engines with Spark
Evolving Databases for New-Gen Big Data Applications
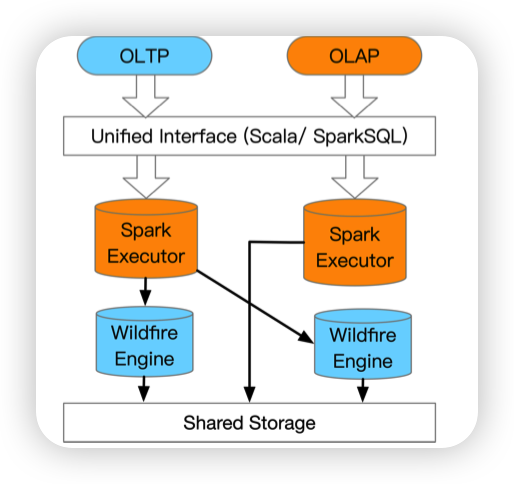
这里看起来像是让SparkExecutor传给Wildfrie Engine做TP。不太清楚是怎么转化的。
Wildfrie Engine应该是事务和缓存层。然后向共享存储中写数据。
HTAP Techniques
对应了刚才提出的挑战,技术分为5种:
- Transaction Processing: updating the row store and writing the delta store
- Analytical Processing: scanning the column store with delta store
- Data Synchronization: merging the delta data to column store
- Query Optimization: planning queries against row store and column store
- Resource Scheduling: scheduling resources for OLTP and OLAP instances
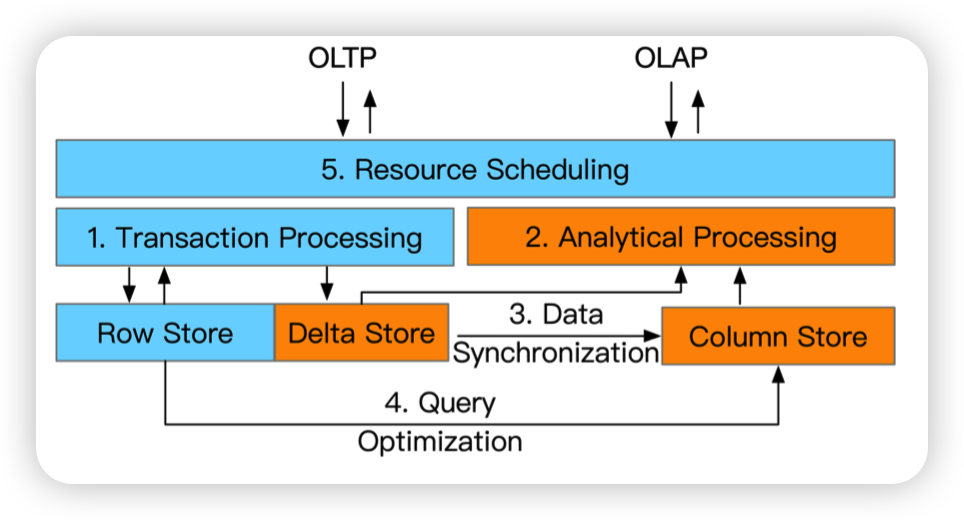
一个一个看一下
Transaction Processing
Standalone TP for insert/delete/update operations
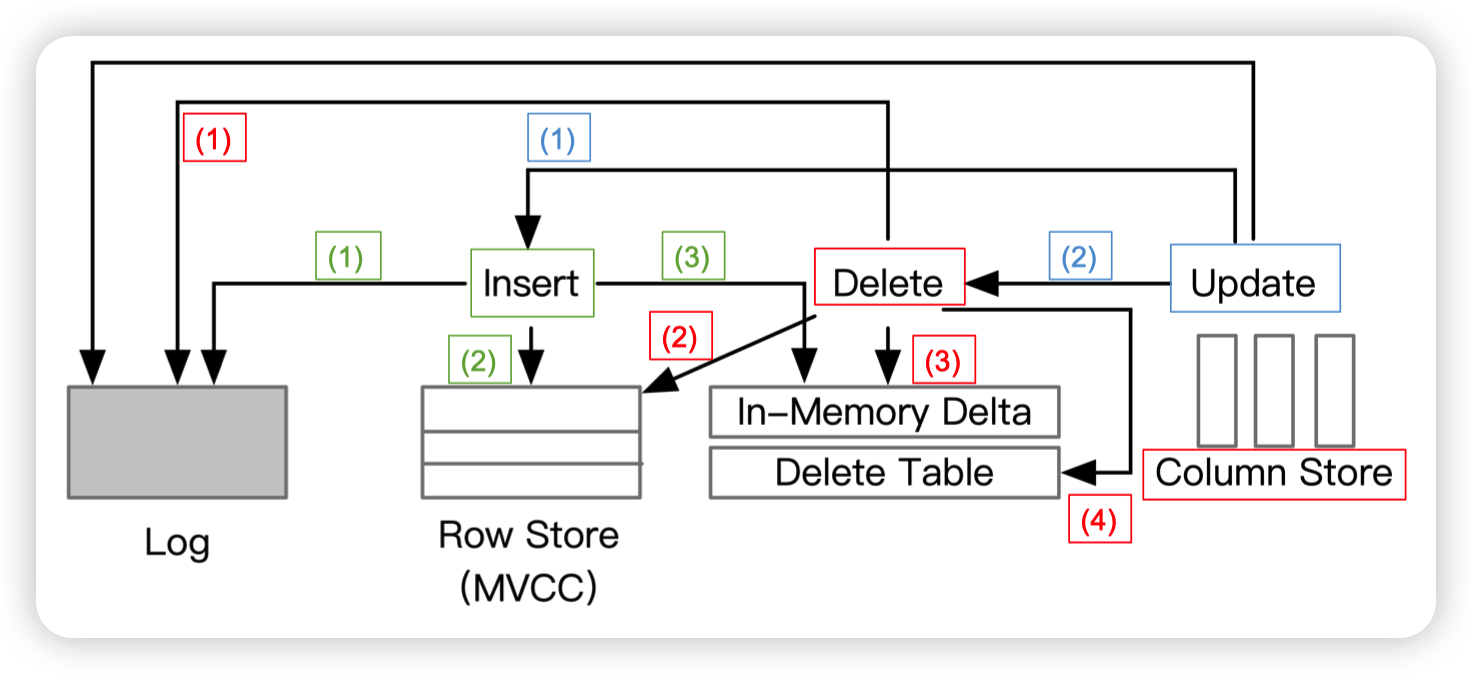
第一步写入到log,第二步更新RowStore,第三步更新delta
delta再merge到column store中
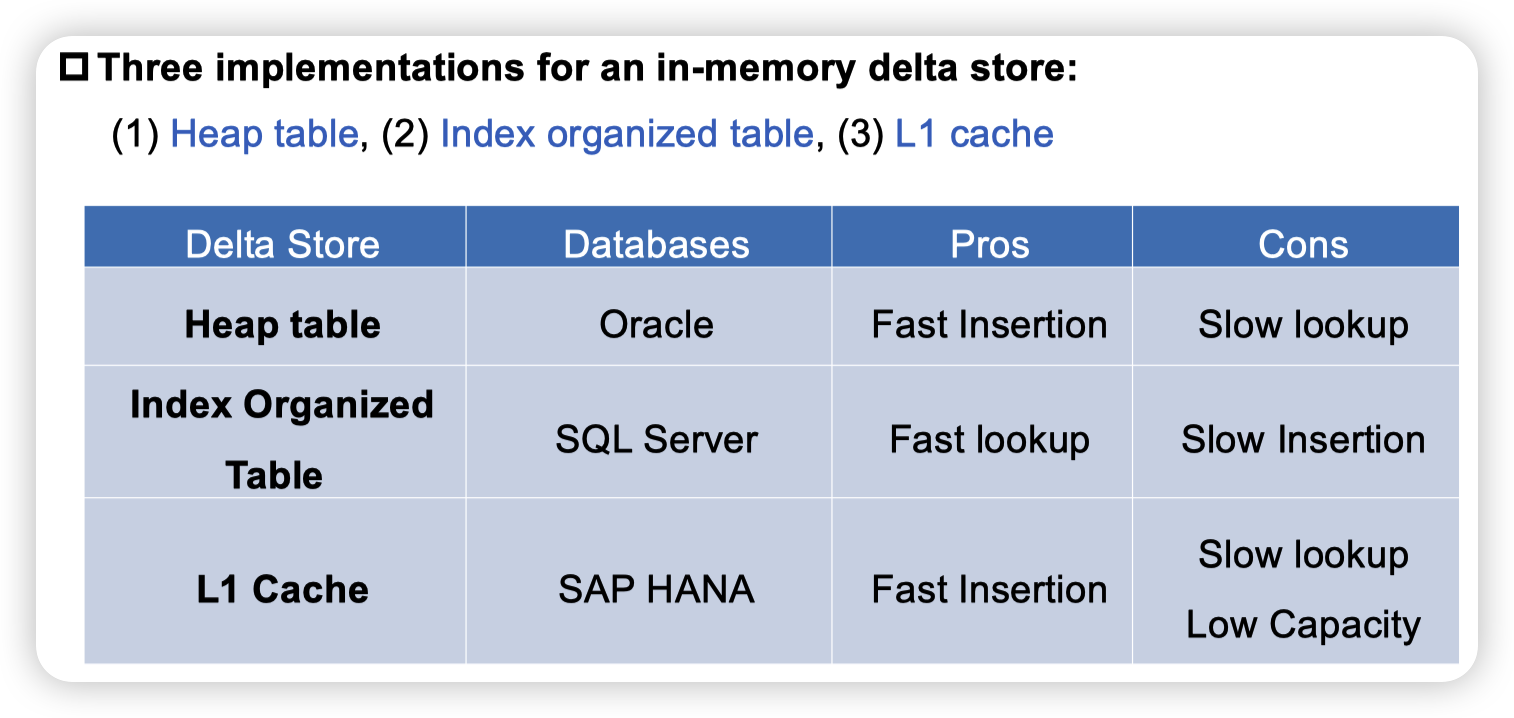
delta store有多中实现方式。猜测SQL Server因为要结合column store和delta store,所以选择了高效的索引结构。而Oracle可能就是单纯的append only
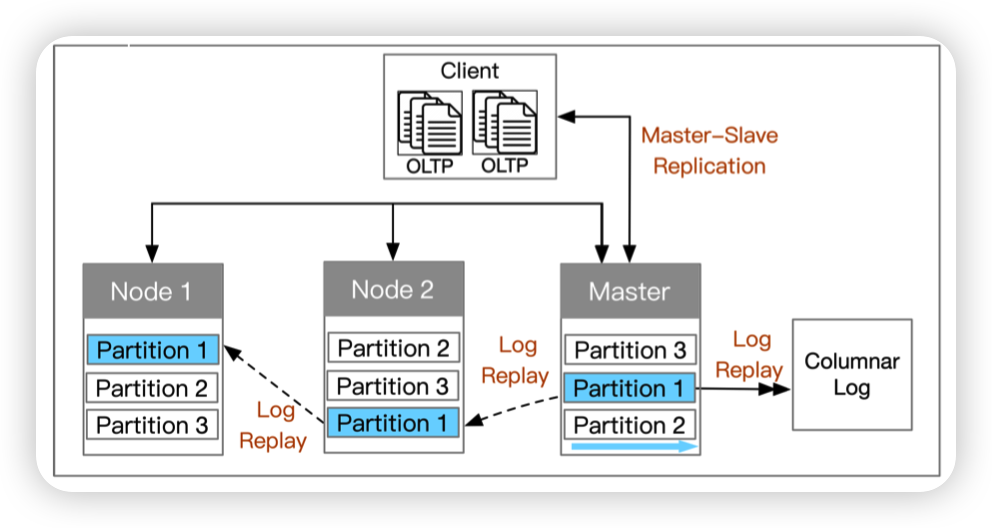
Distributed Transaction Processing with Log Replay
Master负责处理TP请求,然后将log复制给从节点
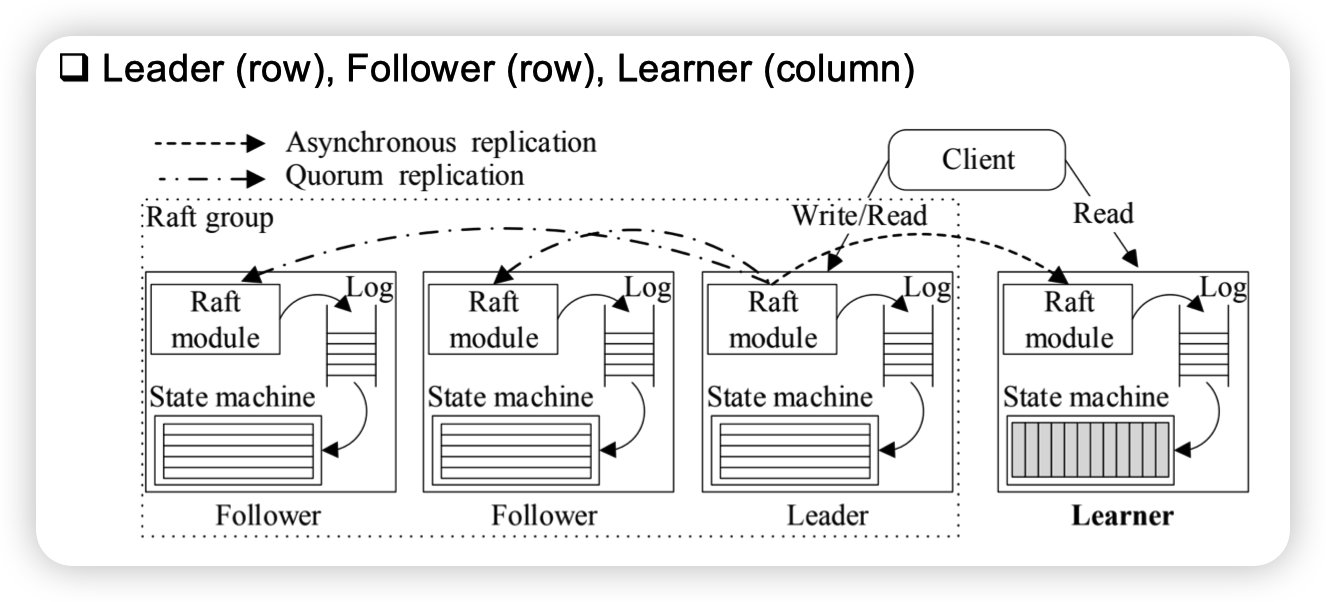
TiDB确实做了TP和AP的融合,但是Learner不作为raft group的成员,只是单纯的重放日志
Analytical Processing
Standalone Columnar Scan with In-Memory Delta Traversing

Distributed Columnar Scan with Log File Scanning
F1 query: Declarative querying at scale
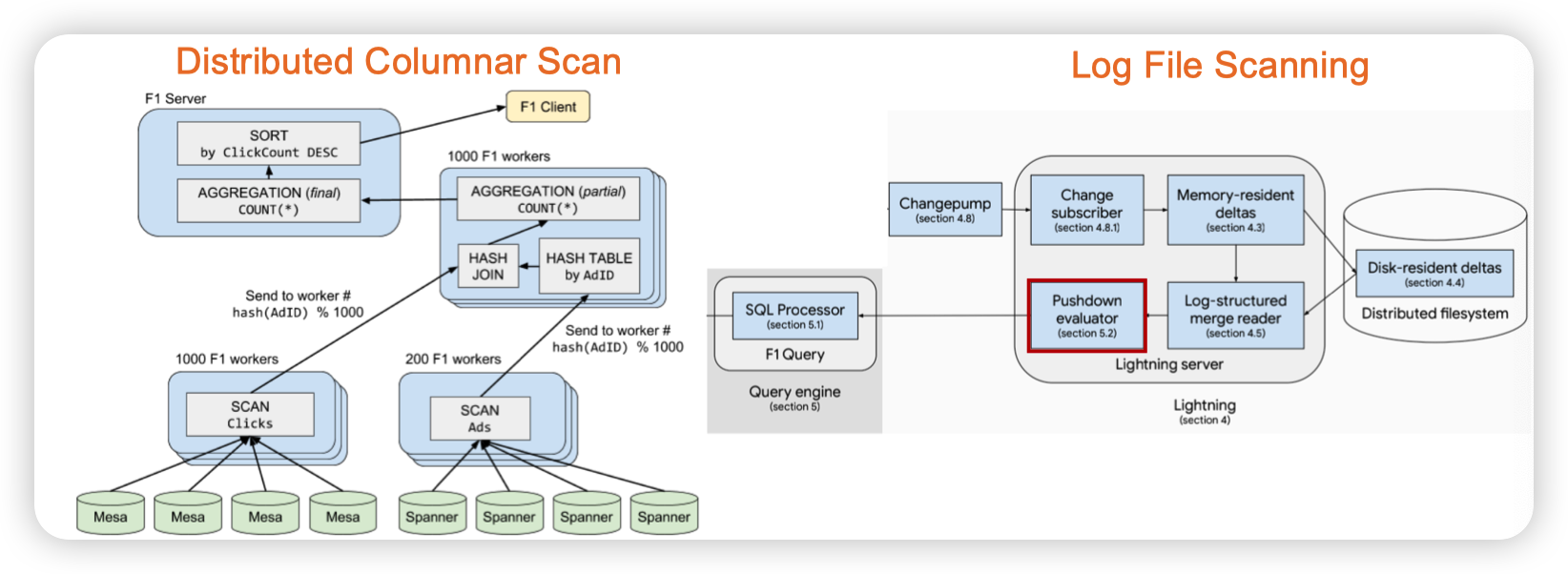
Columnar Scan计算多数数据,然后再从Spanner中订阅的log里去扫描新的数据。
基本思路都是全量 + 追增量
Data Synchronization
In-Memory Delta Merging
- Threshold-based merging
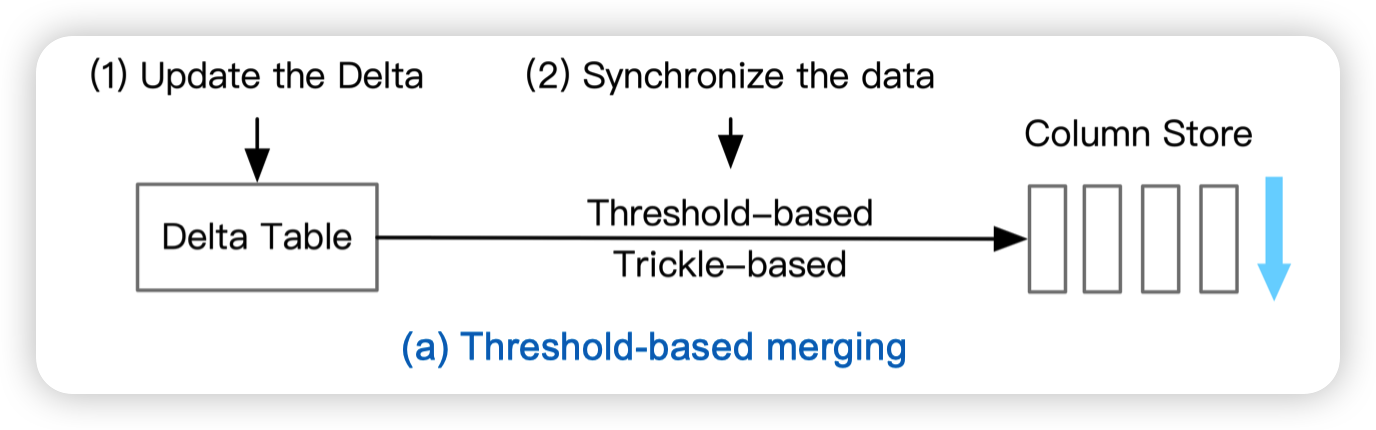
- Tow-phase delta migration

目前还不太清楚,貌似是SQL Server用到的
- Dictionary-based merging
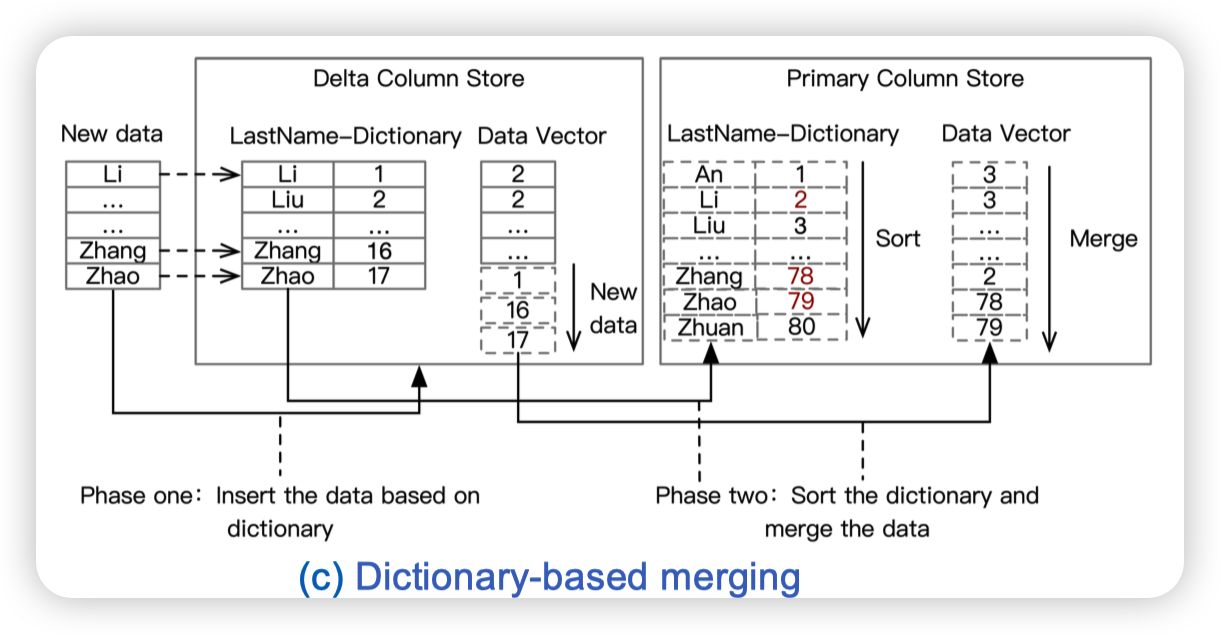
分为两个阶段,第一阶段把新数据插入到字典中。第二阶段和全局的字典做排序,并插入到列存中。
看起来有点诡异...
Log-based delta merge
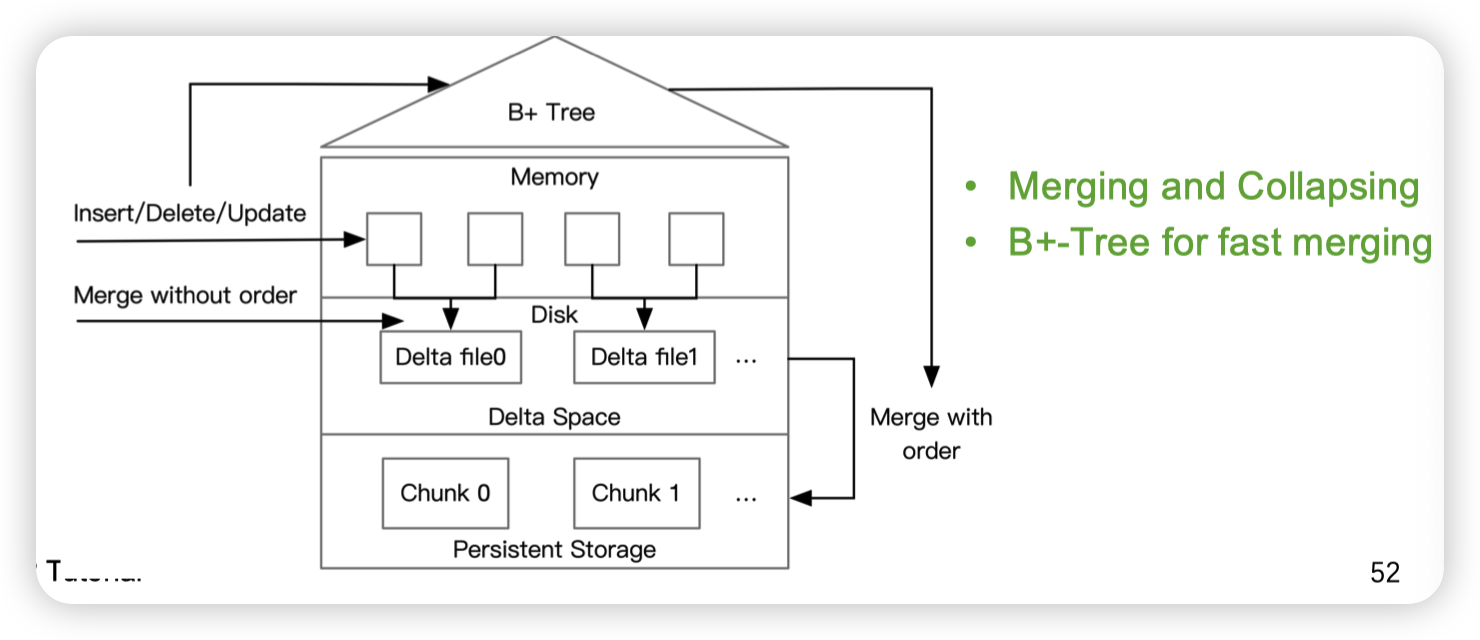
感觉大概的思路就是delta作为L0保存下来。然后合并的时候则是用BTree来提高合并的性能。
后面几个就是偏AP相关的,暂时我也看不太懂,就不在这里罗列了
Other Relevant HTAP Techniques
- Multi-Versioned Indexes for HTAP
On supporting efficient snapshot isolation for hybrid workloads with multi-versioned indexes
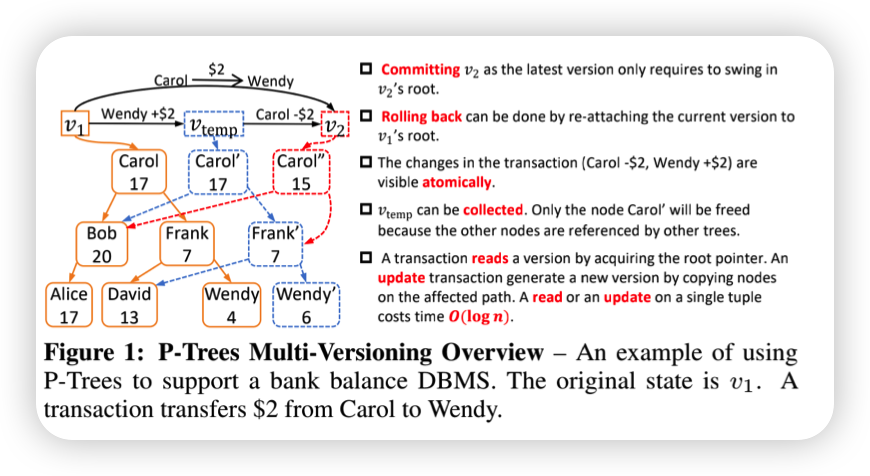
单独看这个图有点像可持久化BTree
MV-PBT: multi-version indexing for large datasets and HTAP workloads
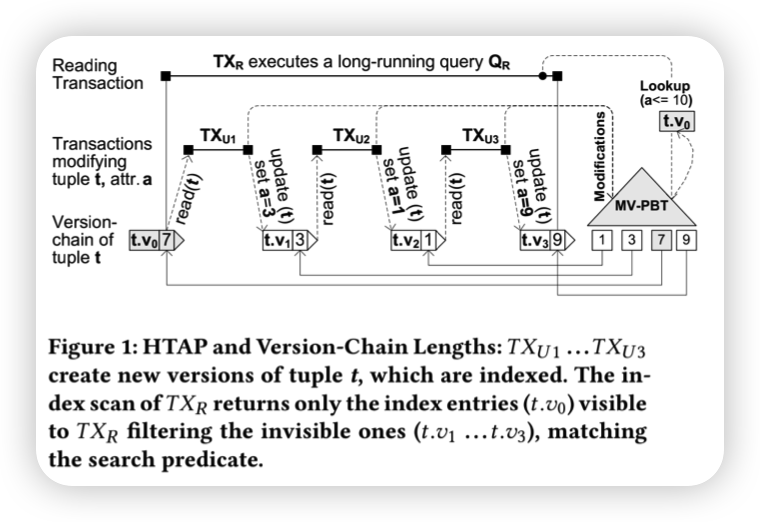
多版本的btree,貌似是在叶子上维护了版本链
Adaptive Data Organization for HTAP
H2O SIGMOD 2014
Casper VLDB 2019
Peloton SIGMOD 2016
Proteus SIGMOD 2022
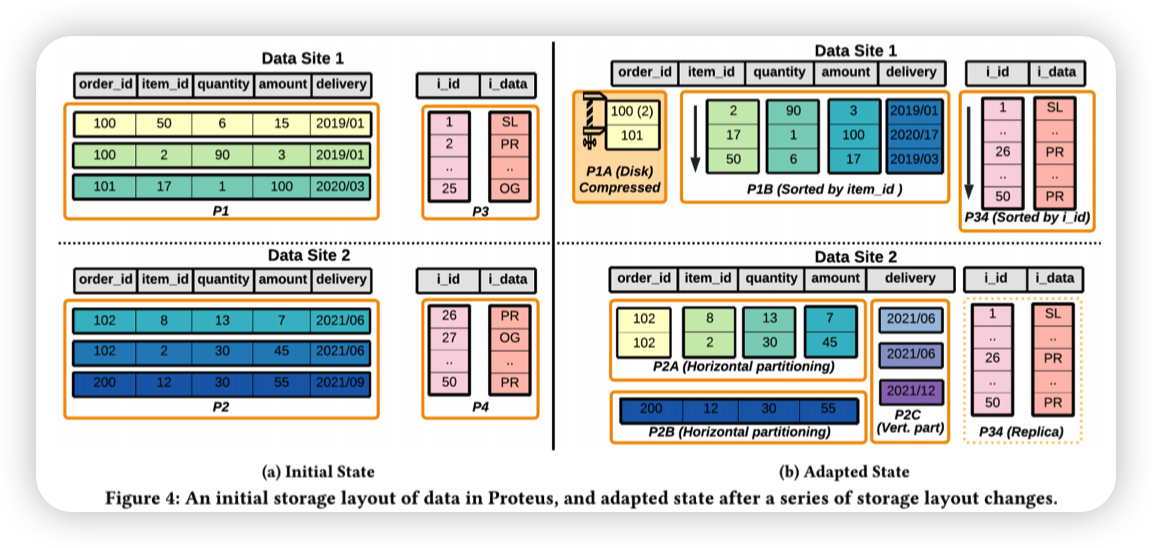
貌似是调整数据的分布。把一些变成列存。或者是混合行列存的方式。
Open Problem
- Primary Row Store for TP, Replicated Column Store for AP
选择那些column被复制?受到memory的限制
- Adaptive Storage for HTAP workloads
调整的复杂度比较高。我个人感觉还有对workload的统计,策略的选择
- Data Synchronization Problem
同步的顺序,什么时候做同步,高效的merge。
可能的方法:Cost Model,对workload的预测,B-tree和LSM-tree做索引的merge。混合merge?比如积累L0文件,在列存的btree上做merge
文章评论
In-Memory Delta Merging确实都是sql server用的,是一个设计的非常好的点,可以很大程度减少migration的时候对tp index的修改导致的对tp流量的影响